Pointer to a Pointer(Double Pointer)
Pointers are used to store the address of other variables of similar datatype. But if you want to store the address of a pointer variable, then you again need a pointer to store it. Thus, when one pointer variable stores the address of another pointer variable, it is known as Pointer to Pointer variable or Double Pointer.
Syntax:
int **p1;Here, we have used two indirection operator(*) which stores and points to the address of a pointer variable i.e, int *. If we want to store the address of this (double pointer) variable p1, then the syntax would become:
int ***p2Simple program to represent Pointer to a Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10;
int *p1; //this can store the address of variable a
int **p2;
/*
this can store the address of pointer variable p1 only.
It cannot store the address of variable 'a'
*/
p1 = &a;
p2 = &p1;
printf("Address of a = %u\n", &a);
printf("Address of p1 = %u\n", &p1);
printf("Address of p2 = %u\n\n", &p2);
// below print statement will give the address of 'a'
printf("Value at the address stored by p2 = %u\n", *p2);
printf("Value at the address stored by p1 = %d\n\n", *p1);
printf("Value of **p2 = %d\n", **p2); //read this *(*p2)
/*
This is not allowed, it will give a compile time error-
p2 = &a;
printf("%u", p2);
*/
return 0;
}Address of a = 2686724 Address of p1 = 2686728 Address of p2 = 2686732 Value at the address stored by p2 = 2686724 Value at the address stored by p1 = 10 Value of **p2 = 10
Explanation of the above program
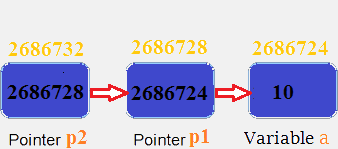
p1pointer variable can only hold the address of the variablea(i.e Number of indirection operator(*)-1 variable). Similarly,p2variable can only hold the address of variablep1. It cannot hold the address of variablea.*p2gives us the value at an address stored by thep2pointer.p2stores the address ofp1pointer and value at the address ofp1is the address of variablea. Thus,*p2prints address ofa.**p2can be read as*(*p2). Hence, it gives us the value stored at the address*p2. From above statement, you know*p2means the address of variable a. Hence, the value at the address*p2is 10. Thus,**p2prints10.